What is an Expansion Joint
WHAT IS A EXPANSION JOINT?
An expansion joint is a mechanical component created to ease the forces caused by expansion, contraction, vibration, and other forms of movement in pipelines.
Although these movements are inevitable, expansion joints work to lessen the strain they impose on the pipeline network and lower the chances of bending, buckling, or separating.
Crafted by the industry’s foremost experts and available in a variety of materials including rubber, PTFE/Teflon®, fabric, and metal, our products are suitable for a broad spectrum of uses.
Pipeline systems naturally expand and contract due to temperature changes, which leads to stress at specific points in the system and within the pipes themselves. While design elements like expansion loops can enhance a pipeline’s flexibility, the addition of expansion joints offers a more cost-effective and efficient method to achieve flexibility while keeping the design compact.
Expansion joints safely absorb both axial and lateral, as well as angular, deflections and can withstand the internal pressures of the pipes. Some of the main advantages of incorporating expansion joints into a pipeline system include:
- Stress reduction: Expansion joints not only relieve the stresses associated with movement within the pipeline but also reduce the strain on connected equipment (such as pumps), which in turn minimizes the likelihood of equipment failure and extends the lifespan of the pipeline system.
- Misalignment adjustment: Certain expansion joints are designed to compensate for misalignments within the pipeline system, varying in degree based on their design. For instance, custom expansion joints may include adjustments to counteract issues related to installation or settling of the pipes.
- Abrasion resistance: Expansion joints can be constructed from a variety of high-performance elastomeric materials that can withstand exposure to abrasive substances.
- Vibration dampening: Expansion joints featuring fatigue-resistant rubber can be strategically placed to absorb vibrations and oscillations.
- Noise reduction: The presence of expansion joints creates a break in the continuity of pipe materials, which aids in reducing the transmission of mechanical noise.
- Shock absorption: Events such as pressure surges, water hammer, and pump cavitation can subject pipelines to various shocks during operation. By absorbing these shocks, expansion joints protect the pipeline system from cumulative damage that could shorten its operational lifespan.
- Lower risk of corrosion: Expansion joints reduce the contact between metal surfaces within the pipeline, eliminating the risk of corrosion when dissimilar metals are joined
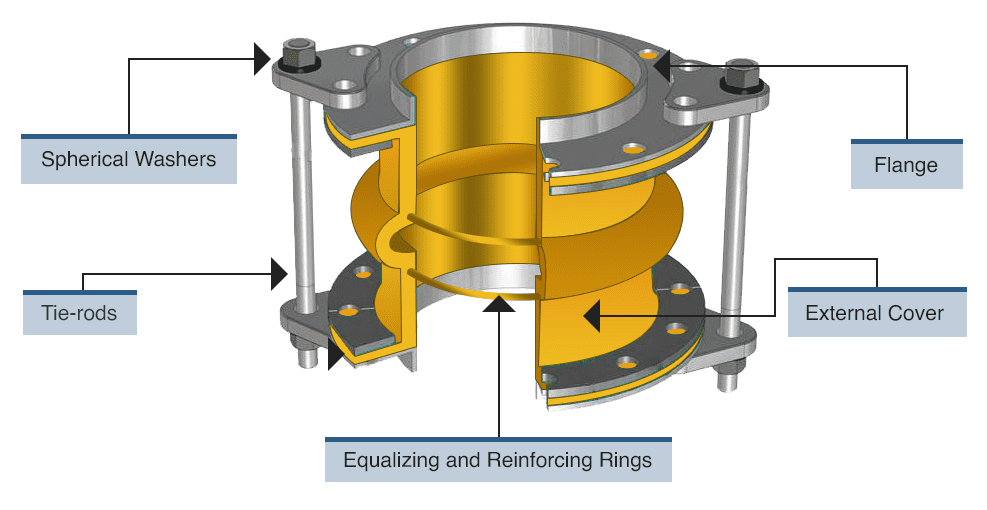
Although the layout of an expansion joint can differ depending on the use case, it typically features a mix of the following elements:
- Inner sleeve
- External cover
- Insulation
- Bellows
- Welding ends
- Flanges
- Hinges
- Tie-rods
- Spherical washers
- Wire mesh
- Equalizing and reinforcing rings
Expansion joints play a crucial role in the structure of piping networks. They are frequently placed close to boilers, pumps, heat exchangers, and various machinery to lessen the strain on pipes at their junctions. Common sectors and uses that depend on them encompass:
- Architecture and civil engineering
- Chemical and oil refining
- Low-temperature cooling operations
- Production of diesel engines
- Components of gas turbines and transmission pipelines
- Steam generators for heat recovery
- Production of pharmaceuticals
- Electricity and combined heat and power systems
- Tanks for high-pressure gases
- Manufacturing of pulp and paper
- Treatment of sewage and wastewater